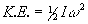Mass Property Results
Mass Property Results
After you select the solid(s) to evaluate, the Mass Properties dialog appears. The following results for each attribute set within the selected solid(s) are displayed in this dialog.
Mass properties will by default calculate using a 'quick calculation' method which speeds up the result time considerably but a recalculate using a more precise method is possible by choosing the Recalculate using a Higher Precision button. Once done the button will be grayed out signifying the calculations where run using the precise method.
Dialog Options:
Mass Property Results:
|
Volume |
Total space occupied by the faceted solid. |
|
Area |
Total area of the faceted solid. |
|
Mass |
The product of Volume times Density. |
|
Surf Mass |
The product of Area times Area Weighted Density. |
You can enter a value signifying an angular velocity about the origin. Angular velocity is used to calculate the following results:
|
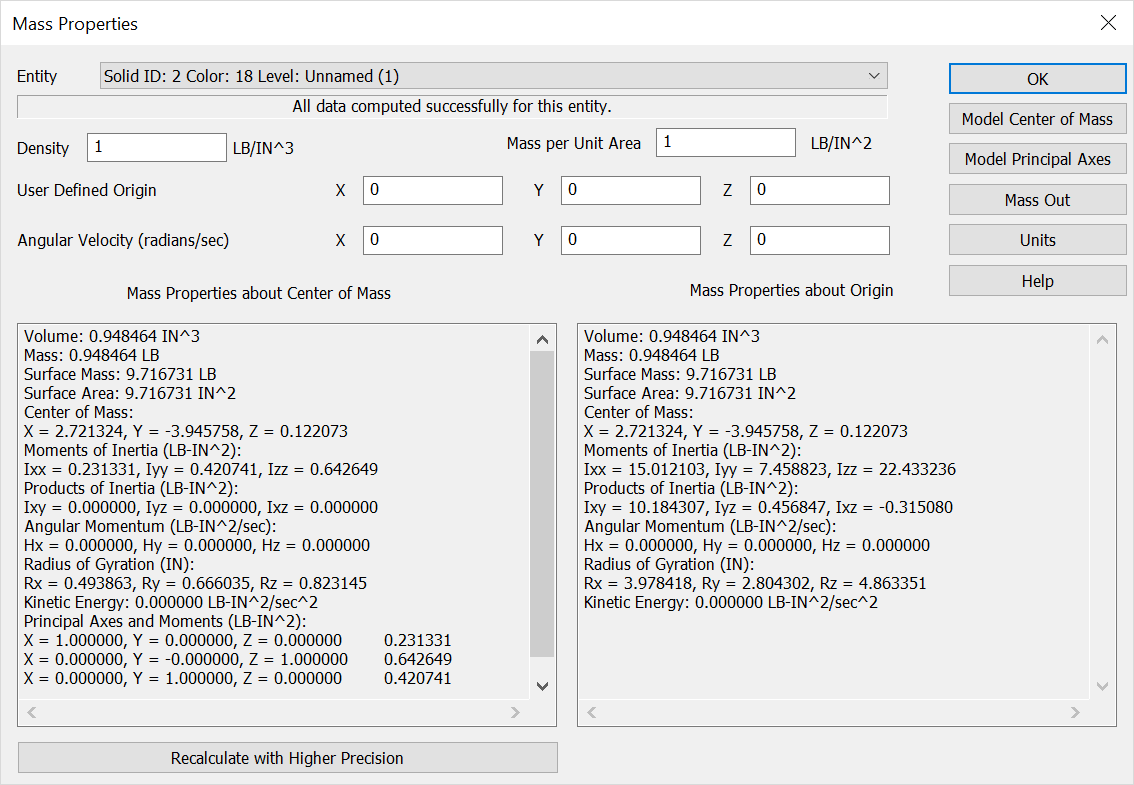
Kinetic Energy |
The energy of a rotating or revolving object:
Where I and omega symbol represent the sum of the moment of inertia about the vector sum of the component angular velocities. This value is calculated from average weighted density and the value you entered for angular velocity. This calculated value refers only to energy due to the object's angular motion. |
|
Moment of Inertia |
The angular equivalent of mass, moment of inertia expresses the resistance of an object to rotational change, or to stopping rotation, about a given axis. |
|
Ixx |
Moment of inertia about the center-of-gravity X axis or an axis parallel to the origin X axis. |
|
Ixy |
Moment of inertia about the diagonal axis in the center-of-gravity XY plane or an axis parallel to the origin XY plane. |
|
Iyy |
Moment of inertia about the center-of-gravity Y axis or an axis parallel to the origin Y axis. |
|
Iyz |
Moment of inertia about the diagonal axis in the center-of-gravity YZ plane or an axis parallel to the origin YZ plane. |
|
Izz |
Moment of inertia about the center-of-gravity Z axis or an axis parallel to the origin Z axis. |
|
Ixz |
Moment of inertia about the diagonal axis in the center-of-gravity XZ plane or an axis parallel to the origin XZ plane. |
|
Angular Momentum |
The resistance to change in angular velocity. This is calculated from the values for moment of inertia, angular velocity, and average weighted density. |
|
Radius of Gyration |
The ratio of moment of inertia to volume. This is the same as the radius of a thin hoop of the same mass that has the same moment of inertia as the object. |
|
Principal Axes |
On any object there will be three mutually perpendicular axes intersecting at the CG for which the products of inertia will be zero. These axes are called the "principal axes." |
|
Principal Moments of Inertia |
The principal moments of inertia are calculated about each of the principal axes. |
Units for Mass Properties Results:
The units of the mass properties results agree with the units of the object properties you enter for each object or attribute set.
For example, if you configure the units of length as centimeters, then the corresponding object data units are as follows:
|
Density |
g/cm3 |
|
Angular Velocity |
radians per second |
|
Volume |
cm3 |
|
Area |
cm2 |
|
Mass |
g |
|
Moment of Inertia |
g(cm)2 |
|
Kinetic Energy |
g(cm2/sec2) |
|
Angular Momentum |
g(cm2/sec) |
|
Radius of Gyration |
cm |