Convert / Measurements / Mass Properties ResultsConvert Mass Properties Results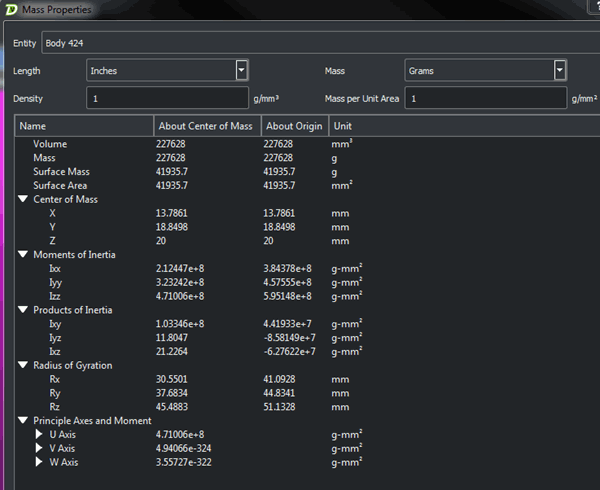 Coordinate Systems
Center of MASS is the unique point at the center of a distribution of mass in space that has the property that the weighted position vectors relative to this point sum to zero (as defined on Wikipedia). Origin is a user defined field which defaults to 0 for XYZ as the reference point.
Basic Measures
Volume — Total area occupied by faceted solid
Mass — The product of volume times density Surface Area — Total area of faceted solid Surface Mass — The product of area times weighted density Measures based on Angular Velocity (XYZ = 0)
Moment/Product of Inertia — Angular equivalent of mass, expresses resistance of an object to rotational change about a given axis
Radius of Gyration — Defined as the radial distance to a point which would have a moment of inertia the same as the body's actual distribution of mass, if the total mass of the body were concentrated ( as defined on Wikipedia).
Principal AXES/Moment — On any object there are three mutually perpendicular axis intersecting at the center of mass for which the products of inertia will be 0, grouped as Principal AXES and the principal moments are calculated about the Principal AXES |